Blank IRS 941 Template
The IRS Form 941 is a crucial document for employers in the United States, serving as a quarterly tax return that reports income taxes, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax withheld from employee paychecks. Each quarter, businesses must accurately complete and submit this form to ensure compliance with federal tax regulations. The form captures key details, including the total wages paid to employees, the amount of taxes withheld, and any adjustments for the current quarter. Additionally, it allows employers to report any tax credits they may be eligible for, such as the Employee Retention Credit. Filing Form 941 is not just a regulatory requirement; it also helps businesses keep track of their tax obligations and ensures that employees' contributions to Social Security and Medicare are properly recorded. Understanding the nuances of this form is essential for maintaining good standing with the IRS and avoiding potential penalties.
Document Example
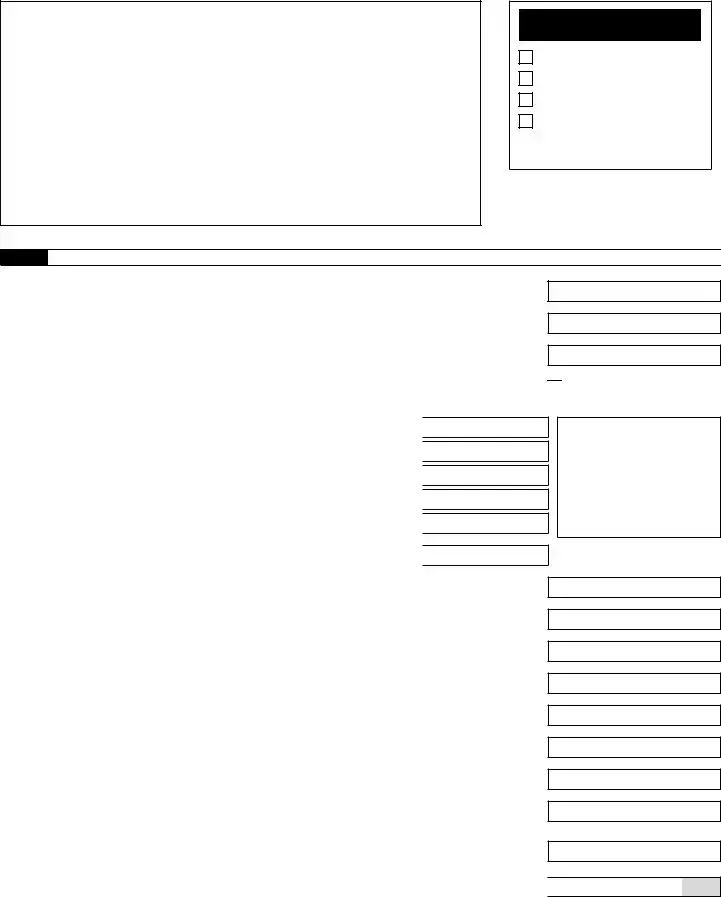
Form 941 for 2023: |
Employer’s QUARTERLY Federal Tax Return |
950122 |
|
|
|
(Rev. March 2023) |
Department of the Treasury — Internal Revenue Service |
OMB No. |
Employer identification number (EIN) |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Name (not your trade name) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trade name (if any) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Address |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
Number |
Street |
|
|
|
|
|
Suite or room number |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
City |
|
|
|
|
State |
|
|
ZIP code |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Foreign country name |
|
|
Foreign province/county |
|
|
Foreign postal code |
||
Report for this Quarter of 2023
(Check one.)
1: January, February, March
2: April, May, June
3: July, August, September
4: October, November, December
Go to www.irs.gov/Form941 for instructions and the latest information.
Read the separate instructions before you complete Form 941. Type or print within the boxes.
Part 1: Answer these questions for this quarter.
1 |
Number of employees who received wages, tips, or other compensation for the pay period |
|
including: Mar. 12 (Quarter 1), June 12 (Quarter 2), Sept. 12 (Quarter 3), or Dec. 12 (Quarter 4) 1 |
2 |
Wages, tips, and other compensation |
. |
2 |
|||||
3 |
Federal income tax withheld from wages, tips, and other compensation |
. |
3 |
|||||
4 |
If no wages, tips, and other compensation are subject to social security or Medicare tax |
|
||||||
|
|
Column 1 |
|
Column 2. |
|
|||
5a |
Taxable social security wages* . . |
. |
× 0.124 = |
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
5a |
(i) |
Qualified sick leave wages* . |
. |
× 0.062 = |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
|
5a |
(ii) |
Qualified family leave wages* . |
. |
× 0.062 = |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
||
5b |
Taxable social security tips . . . |
. |
× 0.124 = |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
. |
|
||
5c |
Taxable Medicare wages & tips. . |
. |
× 0.029 = |
|
|
|||
5d |
Taxable wages & tips subject to |
|
|
|
|
|
||
. |
× 0.009 = |
|
. |
|
||||
|
Additional Medicare Tax withholding |
|
|
|||||
5e |
Total social security and Medicare taxes. Add Column 2 from lines 5a, 5a(i), 5a(ii), 5b, 5c, and 5d |
|
5e |
|||||
5f |
Section 3121(q) Notice and |
. |
5f |
|||||
6 |
Total taxes before adjustments. Add lines 3, 5e, and 5f |
. |
6 |
|||||
7 |
Current quarter’s adjustment for fractions of cents |
. |
7 |
|||||
8 |
Current quarter’s adjustment for sick pay |
. |
8 |
|||||
9 |
Current quarter’s adjustments for tips and |
. |
9 |
|||||
10 |
Total taxes after adjustments. Combine lines 6 through 9 |
. |
10 |
|||||
11a |
Qualified small business payroll tax credit for increasing research activities. Attach Form 8974 |
11a |
||||||
11b |
Nonrefundable portion of credit for qualified sick and family leave wages for leave taken |
|
||||||
|
before April 1, 2021 |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
. |
11b |
||||
.
.

 Check and go to line 6.
Check and go to line 6.
*Include taxable qualified sick and family leave wages paid in this quarter of 2023 for leave taken after March 31, 2021, and before October 1, 2021, on line 5a. Use lines 5a(i) and 5a(ii) only for taxable qualified sick and family leave wages paid in this quarter of 2023 for leave taken after March 31, 2020, and before April 1, 2021.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
11c Reserved for future use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11c 
.
You MUST complete all three pages of Form 941 and SIGN it.
For Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see the back of the Payment Voucher. |
Cat. No. 17001Z |
Form 941 (Rev. |
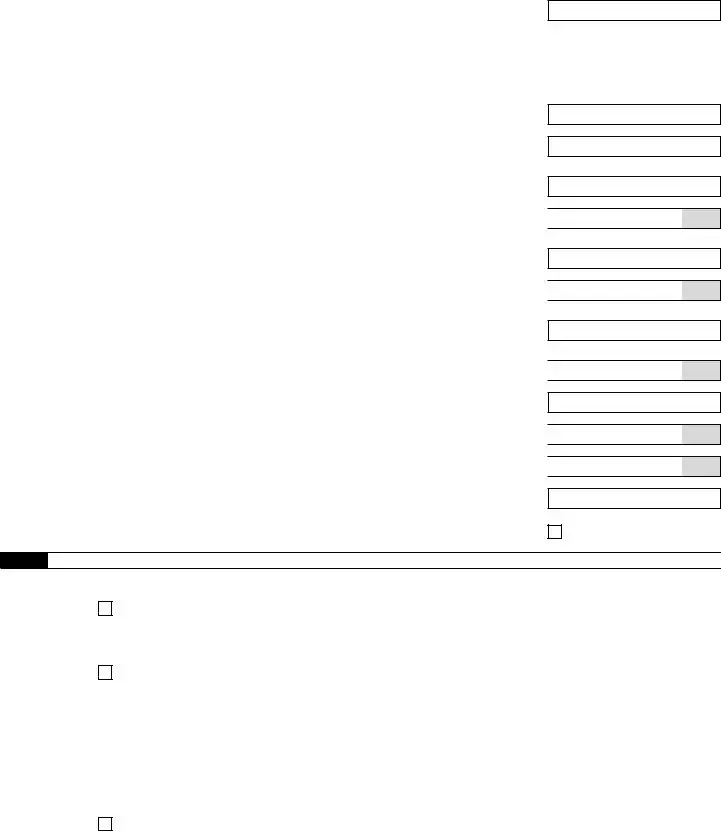
951222
Name (not your trade name) |
Employer identification number (EIN) |
|
|
|
– |
Part 1: |
Answer these questions for this quarter. (continued) |
|
11d Nonrefundable portion of credit for qualified sick and family leave wages for leave taken after March 31, 2021, and before October 1, 2021 . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11d
.
|
|
|
|
|
11e |
Reserved for future use |
. . . . . . . . . 11e |
. |
|
11f |
Reserved for future use |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
11g |
Total nonrefundable credits. Add lines 11a, 11b, and 11d |
11g |
12 |
Total taxes after adjustments and nonrefundable credits. Subtract line 11g from line 10 . |
12 |
.
.
13a |
Total deposits for this quarter, including overpayment applied from a prior quarter and |
|
|
overpayments applied from Form |
13a |
13b |
Reserved for future use |
13b |
.
 .
.
13c Refundable portion of credit for qualified sick and family leave wages for leave taken |
|
before April 1, 2021 |
13c |
13d Reserved for future use |
13d |
.
 .
.
13e Refundable portion of credit for qualified sick and family leave wages for leave taken after March 31, 2021, and before October 1, 2021 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13e
.
13f |
Reserved for future use |
13f |
13g |
Total deposits and refundable credits. Add lines 13a, 13c, and 13e |
13g |
13h |
Reserved for future use |
13h |
13i |
Reserved for future use |
13i |
14Balance due. If line 12 is more than line 13g, enter the difference and see instructions . . . 14
|
|
|
|
15 |
Overpayment. If line 13g is more than line 12, enter the difference |
. |
Check one: |
 .
.
.
 .
.
 .
.
.
Apply to next return. |
|
Send a refund. |
Part 2: Tell us about your deposit schedule and tax liability for this quarter.
If you’re unsure about whether you’re a monthly schedule depositor or a semiweekly schedule depositor, see section 11 of Pub. 15.
16 Check one:
Line 12 on this return is less than $2,500 or line 12 on the return for the prior quarter was less than $2,500, and you didn’t incur a $100,000
You were a monthly schedule depositor for the entire quarter. Enter your tax liability for each month and total
liability for the quarter, then go to Part 3.
|
|
|
Tax liability: Month 1 |
. |
|
|
|
|
Month 2 |
. |
|
|
|
|
Month 3 |
. |
|
|
|
|
Total liability for quarter |
. |
Total must equal line 12. |
You were a semiweekly schedule depositor for any part of this quarter. Complete Schedule B (Form 941),
Report of Tax Liability for Semiweekly Schedule Depositors, and attach it to Form 941. Go to Part 3.
You MUST complete all three pages of Form 941 and SIGN it.
Page 2 |
Form 941 (Rev. |
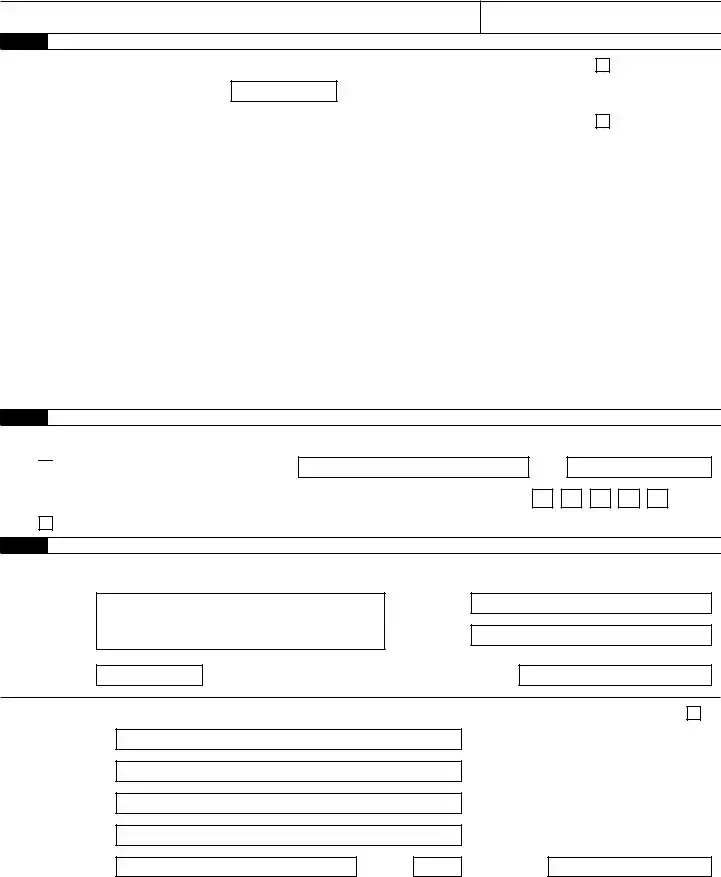
950922
Name (not your trade name)
Employer identification number (EIN)
–
Part 3: Tell us about your business. If a question does NOT apply to your business, leave it blank.
17 If your business has closed or you stopped paying wages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Check here, and
enter the final date you paid wages
/ /
; also attach a statement to your return. See instructions.
18 If you’re a seasonal employer and you don’t have to file a return for every quarter of the year . . .
Check here.
19Qualified health plan expenses allocable to qualified sick leave wages for leave taken before April 1, 2021
20Qualified health plan expenses allocable to qualified family leave wages for leave taken before April 1, 2021
21 |
Reserved for future use |
22 |
Reserved for future use |
23Qualified sick leave wages for leave taken after March 31, 2021, and before October 1, 2021
24Qualified health plan expenses allocable to qualified sick leave wages reported on line 23
25Amounts under certain collectively bargained agreements allocable to qualified sick
leave wages reported on line 23 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
26Qualified family leave wages for leave taken after March 31, 2021, and before October 1, 2021
27Qualified health plan expenses allocable to qualified family leave wages reported on line 26
28Amounts under certain collectively bargained agreements allocable to qualified family leave wages reported on line 26 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
|
|
19 |
. |
|
|
20 |
. |
|
|
21 |
. |
|
|
22 |
. |
|
|
23 |
. |
|
|
24 |
. |
|
|
25 |
. |
|
|
26 |
. |
|
|
27 |
. |
|
|
28 |
. |
Part 4: May we speak with your
Do you want to allow an employee, a paid tax preparer, or another person to discuss this return with the IRS? See the instructions
for details.

 Yes. Designee’s name and phone number
Yes. Designee’s name and phone number
Select a
No.
Part 5: Sign here. You MUST complete all three pages of Form 941 and SIGN it.
Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined this return, including accompanying schedules and statements, and to the best of my knowledge and belief, it is true, correct, and complete. Declaration of preparer (other than taxpayer) is based on all information of which preparer has any knowledge.
Sign your name here
Date
/ /
Print your name here
Print your title here
Best daytime phone
Paid Preparer Use Only
Preparer’s name
Preparer’s signature
Firm’s name (or yours if
Address
City
State
Check if you’re
PTIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Date |
/ |
/ |
|
EIN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Phone |
|
|
|
|
|
|
ZIP code
Page 3 |
Form 941 (Rev. |
951020
This page intentionally left blank

Form
Purpose of Form
Complete Form
Making Payments With Form 941
To avoid a penalty, make your payment with Form 941 only if:
•Your total taxes after adjustments and nonrefundable credits (Form 941, line 12) for either the current quarter or the preceding quarter are less than $2,500, you didn’t incur a $100,000
•You’re a monthly schedule depositor making a payment in accordance with the Accuracy of Deposits Rule. See section 11 of Pub. 15 for details. In this case, the amount of your payment may be $2,500 or more.
Otherwise, you must make deposits by electronic funds transfer. See section 11 of Pub. 15 for deposit instructions. Don’t use Form
▲! Use Form
CAUTION Form 941 that should’ve been deposited, you may be subject to a penalty. See Deposit Penalties in section 11 of Pub. 15.
Specific Instructions
Box
Box
Box
Box
•Enclose your check or money order made payable to “United States Treasury.” Be sure to enter your
EIN, “Form 941,” and the tax period (“1st Quarter 2023,” “2nd Quarter 2023,” “3rd Quarter 2023,” or “4th Quarter 2023”) on your check or money order. Don’t send cash.
Don’t staple Form
•Detach Form
and Form 941 to the address in the Instructions for Form 941.
Note: You must also complete the entity information above Part 1 on Form 941.
Detach Here and Mail With Your Payment and Form 941.
Form |
|
|
|
|
Payment Voucher |
|
OMB No. |
||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Department of the Treasury |
|
|
Don’t staple this voucher or your payment to Form 941. |
|
2023 |
|||||
|
Internal Revenue Service |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
1 Enter your employer identification |
|
2 |
|
Dollars |
|
|
Cents |
|||
|
|
number (EIN). |
|
|
Enter the amount of your payment. |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
– |
|
|
Make your check or money order payable to “United States Treasury.” |
|
|
|
|||
3 |
Tax Period |
|
4 Enter your business name (individual name if sole proprietor). |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1st |
|
3rd |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Quarter |
|
Quarter |
|
Enter your address. |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
2nd |
|
4th |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
Enter your city, state, and ZIP code; or your city, foreign country name, foreign province/county, and foreign postal code. |
|||||||
|
|
Quarter |
|
Quarter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

Form 941 (Rev.
Privacy Act and Paperwork Reduction Act Notice. We ask for the information on Form 941 to carry out the Internal Revenue laws of the United States. We need it to figure and collect the right amount of tax. Subtitle C, Employment Taxes, of the Internal Revenue Code imposes employment taxes on wages and provides for income tax withholding. Form 941 is used to determine the amount of taxes that you owe. Section 6011 requires you to provide the requested information if the tax is applicable to you. Section 6109 requires you to provide your identification number. If you fail to provide this information in a timely manner, or provide false or fraudulent information, you may be subject to penalties.
You’re not required to provide the information requested on a form that is subject to the Paperwork Reduction Act unless the form displays a valid OMB control number. Books and records relating to a form or its instructions must be retained as long as their contents may become material in the administration of any Internal Revenue law.
Generally, tax returns and return information are confidential, as required by section 6103. However, section 6103 allows or requires the IRS to disclose or give the information shown on your tax return to others as described in the Code. For example, we may disclose your tax information to the Department of
Justice for civil and criminal litigation, and to cities, states, the District of Columbia, and U.S. commonwealths and possessions for use in administering their tax laws. We may also disclose this information to other countries under a tax treaty, to federal and state agencies to enforce federal nontax criminal laws, or to federal law enforcement and intelligence agencies to combat terrorism.
The time needed to complete and file Form 941 will vary depending on individual circumstances. The estimated average time is:
Recordkeeping . . . . . . . . . . 22 hr., 28 min.
Learning about the law or the form . . |
. . 53 min. |
Preparing, copying, assembling, and |
|
sending the form to the IRS |
1 hr., 18 min. |
If you have comments concerning the accuracy of these time estimates or suggestions for making Form 941 simpler, we would be happy to hear from you. You can send us comments from www.irs.gov/FormComments. Or you can send your comments to Internal Revenue Service, Tax Forms and Publications Division, 1111 Constitution Ave. NW,
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the IRS Form 941?
The IRS Form 941, officially known as the Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return, is a form that employers use to report income taxes, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax withheld from employee paychecks. This form is filed quarterly, and it helps the IRS track the amount of payroll taxes that employers are required to pay.
-
Who needs to file Form 941?
Any employer who pays wages to employees must file Form 941. This includes businesses, non-profit organizations, and government entities. If you have employees and withhold federal income tax or Social Security and Medicare taxes from their wages, you are required to submit this form.
-
When is Form 941 due?
Form 941 is due four times a year, at the end of each quarter. The deadlines for filing are:
- April 30 for the first quarter (January to March)
- July 31 for the second quarter (April to June)
- October 31 for the third quarter (July to September)
- January 31 for the fourth quarter (October to December)
Filing on time is crucial to avoid penalties and interest on any taxes owed.
-
What information do I need to complete Form 941?
To fill out Form 941, you will need various pieces of information, including:
- Your business name and address
- Your Employer Identification Number (EIN)
- The total number of employees
- The total wages paid to employees
- The amount of federal income tax withheld
- The amount of Social Security and Medicare taxes withheld
Accurate information ensures that you comply with tax regulations and helps avoid discrepancies with the IRS.
-
What happens if I don’t file Form 941?
Failing to file Form 941 can lead to significant consequences. The IRS may impose penalties for late filing, which can accumulate over time. Additionally, if you do not pay the taxes owed, interest will accrue on the unpaid balance. Continuous failure to file can result in further legal actions, including liens or levies against your business assets.
Misconceptions
-
Misconception 1: The IRS 941 form is only for large businesses.
This is not true. The IRS 941 form is required for all employers who pay wages to employees. Whether you run a small business or a large corporation, if you have employees, you need to file this form.
-
Misconception 2: You can skip filing the IRS 941 form if you didn’t have any employees during a quarter.
This is incorrect. Even if you didn’t have any employees during a specific quarter, you still need to file the form. It’s important to report your status to the IRS to avoid penalties.
-
Misconception 3: The IRS 941 form is only about income tax withholding.
This is a common misunderstanding. While the form does cover income tax withholding, it also addresses Social Security and Medicare taxes. All these components are essential for accurate reporting.
-
Misconception 4: You can file the IRS 941 form at any time during the year.
This is misleading. The IRS has specific deadlines for filing the 941 form, typically on a quarterly basis. Missing these deadlines can lead to penalties, so it's crucial to stay on schedule.
Common mistakes
-
Incorrect Employer Identification Number (EIN): One common mistake is entering the wrong EIN. This number is crucial for identifying your business with the IRS. Double-checking this number before submission can save you from delays or issues.
-
Omitting Wages and Tax Amounts: Failing to accurately report wages and tax amounts is another frequent error. Make sure to include all applicable wages and the corresponding taxes withheld. Inaccuracies can lead to penalties or audits.
-
Not Signing the Form: It may seem simple, but forgetting to sign the form can cause significant problems. The IRS requires a signature to validate the submission. Always review the form to ensure it is signed before sending it in.
-
Using the Wrong Tax Period: Some people mistakenly file for the wrong tax period. Each quarter has specific due dates and forms. Ensure you are using the correct form for the quarter you are reporting.
Additional PDF Templates
Load Calculations - The form assists in evaluating residential and commercial load needs.
In addition to preparing for your future, understanding the nuances of a prenuptial agreement is essential, as it not only safeguards your interests but also clarifies financial responsibilities; for more comprehensive information, you can refer to All Arizona Forms.
Dh 680 Form - Immunization compliance is essential for participating in school activities in Florida.
Document Data
| Fact Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The IRS Form 941 is used to report employment taxes, including federal income tax withheld and Social Security and Medicare taxes. |
| Filing Frequency | This form must be filed quarterly by employers who withhold income and payroll taxes from their employees' wages. |
| Due Dates | Form 941 is due on the last day of the month following the end of the quarter. For example, the due date for Q1 is April 30. |
| Penalties | Failure to file on time may result in penalties. The IRS can impose fines for late submissions and underpayment of taxes. |
| State-Specific Forms | Some states require additional forms for employment taxes. For example, California requires Form DE 9, governed by California Revenue and Taxation Code. |
| Electronic Filing | Employers can file Form 941 electronically using the IRS e-file system, which can speed up processing times. |
| Recordkeeping | Employers must keep records of wages paid and taxes withheld for at least four years after filing Form 941. |
Similar forms
The IRS Form 940 is a similar document to the IRS 941, focusing on unemployment taxes. While Form 941 is used to report income taxes, Social Security, and Medicare taxes withheld from employees’ wages, Form 940 specifically addresses the Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA). Employers file this form annually to report and pay unemployment taxes for their employees. Both forms require detailed information about employee wages, but Form 940 is concerned with the employer's tax obligations rather than withholding taxes from employee paychecks.
Form W-2 is another document that shares similarities with Form 941, as both are related to employee wages and tax reporting. The W-2 form is used by employers to report an employee's annual wages and the taxes withheld from their pay. While Form 941 is filed quarterly to report the amounts withheld during that period, Form W-2 is issued annually to employees, summarizing their total earnings and tax withholdings for the year. Both forms are crucial for ensuring that employees accurately report their income when filing their personal tax returns.
Form W-3 complements Form W-2 and serves as a summary of all W-2 forms submitted by an employer. This document is filed with the Social Security Administration and provides a total of all wages, tips, and other compensation paid to employees, as well as the total taxes withheld. Similar to Form 941, which aggregates quarterly tax liabilities, Form W-3 consolidates annual data, making it easier for the IRS to track and verify tax information reported by employers.
Form 1099-MISC is another document that aligns with Form 941 in the context of reporting income. While Form 941 is specifically for employees, Form 1099-MISC is used to report payments made to independent contractors or freelancers. Businesses must file this form when they pay $600 or more to a non-employee for services. Both forms require accurate reporting of payments made, but they serve different purposes based on the employment classification of the individual receiving the payment.
Form 944 is designed for smaller employers and functions similarly to Form 941. Employers who expect to owe less than $1,000 in payroll taxes for the year can file Form 944 annually instead of quarterly. This form simplifies the reporting process for small businesses by allowing them to submit their payroll tax information just once a year, while Form 941 requires quarterly submissions. Both forms serve to report income taxes withheld, Social Security, and Medicare taxes, but they cater to different employer sizes and tax obligations.
Form 945 is another related document, which is used to report federal income tax withheld from non-payroll payments. While Form 941 covers taxes withheld from employee wages, Form 945 is for reporting taxes withheld from other types of payments, such as pensions, annuities, and certain gambling winnings. Both forms are essential for ensuring compliance with federal tax regulations, but they apply to different types of payments and withholding scenarios.
Form 8862, while not a direct payroll tax form, is relevant for individuals claiming the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) after having been disqualified in previous years. This form is filed by individuals who wish to claim the EITC again and must provide information about their income and tax situation. Although Form 941 is primarily for employer reporting, both forms ultimately contribute to the broader tax compliance landscape, affecting how individuals and businesses navigate their tax responsibilities.
Understanding the various forms required by the IRS is crucial for compliance. Among them, the Georgia Bill of Sale form plays a significant role in documenting important transactions and can be accessed at onlinelawdocs.com. This form not only serves as proof of ownership transfer, but it also aids in ensuring that all parties involved are protected during the sale process.
Form 1040 is the individual income tax return form that all taxpayers must file annually. While it serves a different purpose from Form 941, both forms are interconnected in the sense that the information reported on Form 941 impacts the employee’s income reported on Form 1040. Employees rely on the accuracy of the information on their W-2s, which are generated based on the data reported in Form 941. Both forms are critical for ensuring that individuals fulfill their tax obligations and receive any applicable credits or refunds.
Finally, Form 1095-C is relevant for employers offering health insurance coverage to their employees. This form is used to report information about health insurance coverage offered to full-time employees under the Affordable Care Act. While Form 941 focuses on payroll taxes, both forms are essential for compliance with federal regulations. Employers must accurately report employee information on both forms to ensure that they meet their obligations under tax and healthcare laws.
