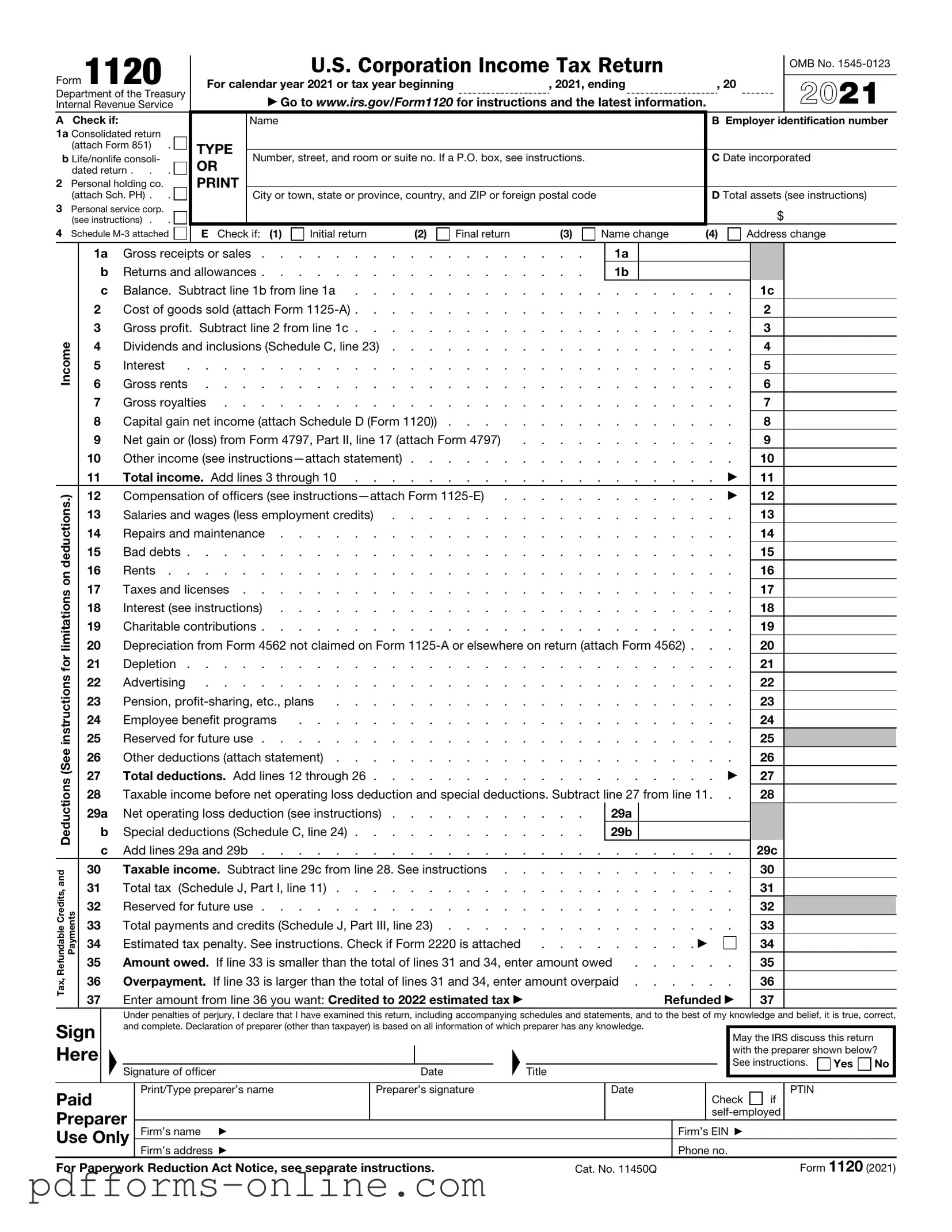
Blank IRS 1120 Template
The IRS 1120 form is a crucial document for corporations operating in the United States, serving as their annual income tax return. This form allows corporations to report their income, calculate their tax liability, and disclose various deductions and credits. It's not just a simple filing; it's a comprehensive overview of a corporation's financial health for the year. Corporations must provide detailed information about their revenue, expenses, and any applicable tax credits. Additionally, the form requires disclosure of ownership and any changes in corporate structure, which can significantly impact tax obligations. Understanding the nuances of the IRS 1120 form is essential for compliance and to avoid potential penalties. As the deadline approaches, corporations must ensure that they gather all necessary documentation to accurately complete the form and meet their tax obligations on time. This article will delve into the key components of the IRS 1120 form, its importance, and the steps necessary for successful filing.
Document Example
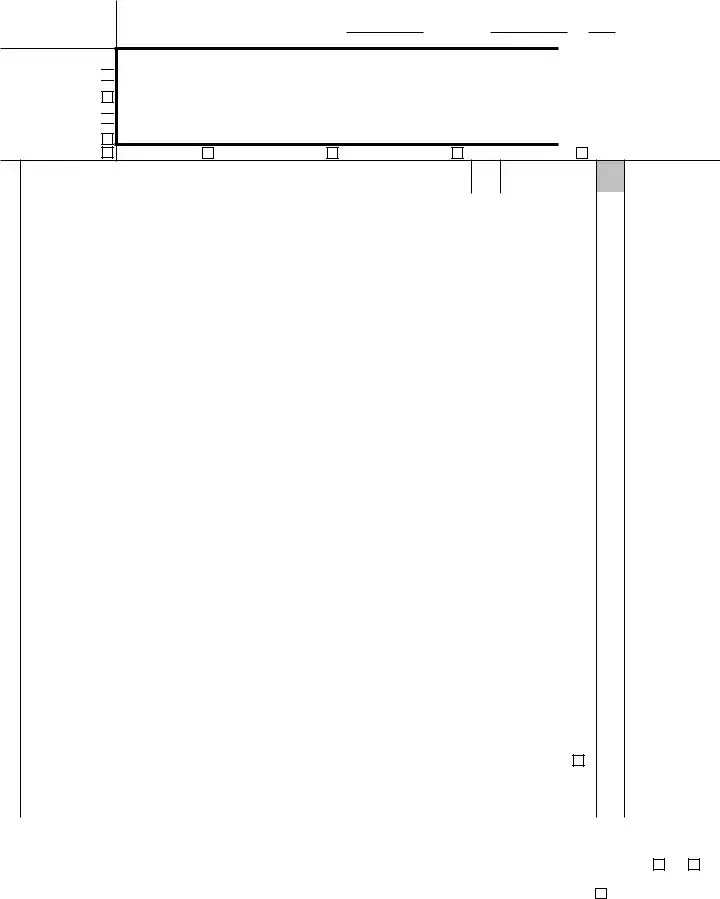
Form 1120
Department of the Treasury
Internal Revenue Service
A Check if:
1a Consolidated return (attach Form 851) . 

b Life/nonlife consoli- dated return . . .
2Personal holding co. (attach Sch. PH) . . 

3Personal service corp. (see instructions) . .
4 Schedule
|
|
U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return |
|
|
OMB No. |
||||
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
For calendar year 2021 or tax year beginning |
|
, 2021, ending |
, 20 |
|
2021 |
||||
|
▶ Go to www.irs.gov/Form1120 for instructions and the latest information. |
|
|||||||
|
Name |
|
|
|
|
|
B Employer identification number |
||
TYPE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Number, street, and room or suite no. If a P.O. box, see instructions. |
|
C Date incorporated |
|||||||
OR |
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
City or town, state or province, country, and ZIP or foreign postal code |
|
D Total assets (see instructions) |
|||||||
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
|
E Check if: (1) |
Initial return |
(2) |
Final return |
(3) |
Name change |
(4) |
Address change |
||
|
1a |
|
Gross receipts or sales |
|
. . . |
. |
|
1a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
b |
|
Returns and allowances |
|
. . . |
. |
|
1b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
c |
|
Balance. Subtract line 1b from line 1a |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
1c |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
2 |
|
|
Cost of goods sold (attach Form |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
2 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
3 |
|
|
Gross profit. Subtract line 2 from line 1c |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
3 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Income |
4 |
|
|
Dividends and inclusions (Schedule C, line 23) |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
4 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
5 |
|
|
Interest |
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
5 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
6 |
|
|
Gross rents |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
6 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
7 |
|
|
Gross royalties |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
7 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
8 |
|
|
Capital gain net income (attach Schedule D (Form 1120)) . . . . |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
8 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
9 |
|
|
Net gain or (loss) from Form 4797, Part II, line 17 (attach Form 4797) |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
9 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
10 |
|
|
Other income (see |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
10 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
11 |
|
|
Total income. Add lines 3 through 10 |
|
. . . |
. |
. . |
. . |
. |
. |
. |
|
▶ |
11 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
deductions.) |
12 |
|
|
Compensation of officers (see |
|
. . . |
. |
. . |
. . |
. |
. |
. |
|
▶ |
12 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
13 |
|
|
Salaries and wages (less employment credits) |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
13 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
14 |
|
|
Repairs and maintenance |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
14 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
15 |
|
|
Bad debts |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
15 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
on |
16 |
|
|
Rents |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
16 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
17 |
|
|
Taxes and licenses |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
17 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
limitations |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
20 |
|
|
Depreciation from Form 4562 not claimed on Form |
20 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
18 |
|
|
Interest (see instructions) |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
18 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
19 |
|
|
Charitable contributions |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
19 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
for |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
21 |
|
|
Depletion |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
21 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
instructions |
25 |
|
|
Reserved for future use |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
25 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
22 |
|
|
Advertising |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
22 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
23 |
|
|
Pension, |
. . . . . . . . . . |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
23 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
24 |
|
|
Employee benefit programs |
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
24 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||
(See |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
26 |
|
|
Other deductions (attach statement) |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
26 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
Deductions |
27 |
|
|
Total deductions. Add lines 12 through 26 |
|
. . . |
. |
. . |
. . |
. |
. |
. |
|
▶ |
27 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||
28 |
|
|
Taxable income before net operating loss deduction and special deductions. Subtract line 27 from line 11. . |
28 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
29a |
|
Net operating loss deduction (see instructions) |
|
. . . |
. |
|
29a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
b |
|
Special deductions (Schedule C, line 24) |
|
. . . |
. |
|
29b |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
c |
|
Add lines 29a and 29b |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
29c |
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
and |
30 |
|
|
Taxable income. Subtract line 29c from line 28. See instructions . |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
30 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
31 |
|
|
Total tax |
(Schedule J, Part I, line 11) |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
31 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
Credits,Refundable Payments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
32 |
|
|
Reserved for future use |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
32 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
33 |
|
|
Total payments and credits (Schedule J, Part III, line 23) . . . . |
|
. . . . . . . . . . . . |
33 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
34 |
|
|
Estimated tax penalty. See instructions. Check if Form 2220 is attached |
. . |
. |
. . |
. . |
. |
. ▶ |
|
|
|
34 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
35 |
|
|
Amount owed. If line 33 is smaller than the total of lines 31 and 34, enter amount owed |
. . . . . . |
35 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Tax, |
36 |
|
|
Overpayment. If line 33 is larger than the total of lines 31 and 34, enter amount overpaid |
36 |
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
37 |
|
|
Enter amount from line 36 you want: Credited to 2022 estimated tax ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Refunded ▶ |
37 |
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
Sign |
|
|
Under penalties of perjury, I declare that I have examined this return, including accompanying schedules and statements, and to the best of my knowledge and belief, it is true, correct, |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
and complete. Declaration of preparer (other than taxpayer) is based on all information of which preparer has any knowledge. |
|
|
|
|
|
May the IRS discuss this return |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
Here |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
with the preparer shown below? |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See instructions. |
Yes |
No |
||
|
|
|
▲Signature of officer |
|
|
|
Date |
▲ |
|
Title |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Paid |
|
|
Print/Type preparer’s name |
|
|
Preparer’s signature |
|
|
|
|
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
Check |
if |
PTIN |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Preparer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Firm’s name ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Firm’s EIN ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Use Only |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
Firm’s address ▶ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Phone no. |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
For Paperwork Reduction Act Notice, see separate instructions. |
|
|
|
Cat. No. 11450Q |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form 1120 (2021) |
|||||||||||||||||
Form 1120 (2021) |
|
|
Page 2 |
|
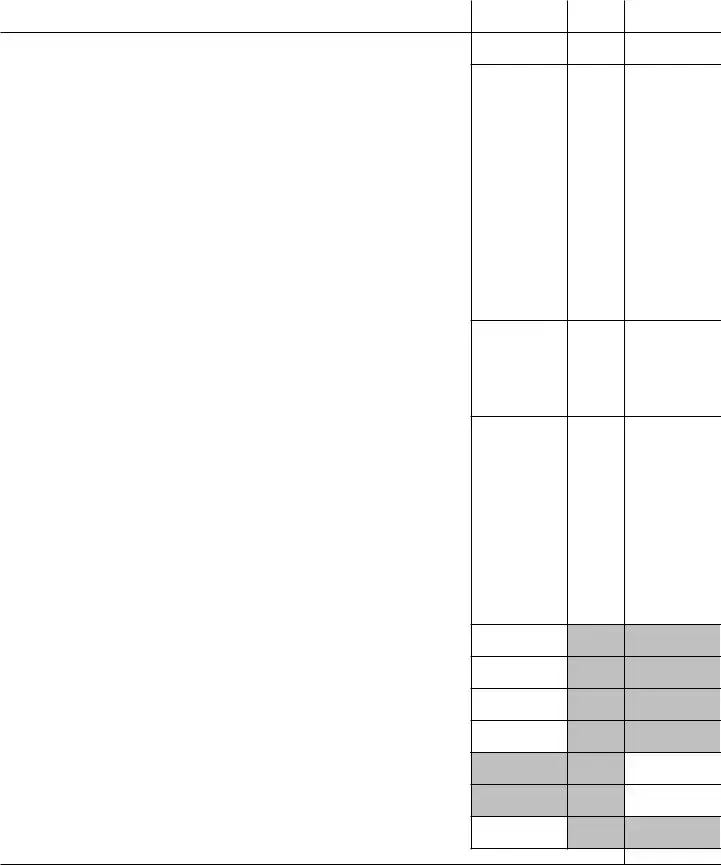
Schedule C |
Dividends, Inclusions, and Special Deductions (see |
(a) Dividends and |
(b) % |
(c) Special deductions |
|
instructions) |
inclusions |
(a) × (b) |
|
|
|
|||
1Dividends from
stock) |
50 |
2Dividends from
|
stock) |
65 |
|
|
See |
3 |
Dividends on certain |
instructions |
4 |
Dividends on certain preferred stock of |
23.3 |
5 |
Dividends on certain preferred stock of |
26.7 |
6 |
Dividends from |
50 |
7 |
Dividends from |
65 |
8 |
Dividends from wholly owned foreign subsidiaries |
100 |
|
|
See |
9 |
Subtotal. Add lines 1 through 8. See instructions for limitations |
instructions |
10Dividends from domestic corporations received by a small business investment
|
company operating under the Small Business Investment Act of 1958 |
100 |
11 |
Dividends from affiliated group members |
100 |
12 |
Dividends from certain FSCs |
100 |
13
|
corporation (excluding hybrid dividends) (see instructions) |
|
100 |
|
|
14 |
Dividends from foreign corporations not included on line 3, 6, 7, 8, 11, 12, or 13 |
|
|
||
|
(including any hybrid dividends) |
|
|
|
|
15 |
Reserved for future use |
|
|
|
|
16a |
Subpart F inclusions derived from the sale by a controlled foreign corporation (CFC) of |
|
|
||
|
the stock of a |
100 |
|
||
|
(see instructions) |
|
|
||
b |
Subpart F inclusions derived from hybrid dividends of tiered corporations (attach Form(s) |
|
|
||
|
5471) (see instructions) |
|
|
|
|
c |
Other inclusions from CFCs under subpart F not included on line 16a, 16b, or 17 (attach |
|
|
||
|
Form(s) 5471) (see instructions) |
|
|
||
17 |
Global Intangible |
18 |
|
19 |
|
20 |
Other dividends |
21 |
Deduction for dividends paid on certain preferred stock of public utilities . . . . |
22 |
Section 250 deduction (attach Form 8993) |
23Total dividends and inclusions. Add column (a), lines 9 through 20. Enter here and on page 1, line 4 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
24 |
Total special deductions. Add column (c), lines 9 through 22. Enter here and on page 1, line 29b |
Form 1120 (2021)

Form 1120 (2021) |
|
|
|
|
|
Page 3 |
|
Schedule J |
Tax Computation and Payment (see instructions) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Part |
|
|
|
|
|
||
1 |
Check if the corporation is a member of a controlled group (attach Schedule O (Form 1120)). See instructions |
▶ |
|
|
|||
2 |
Income tax. See instructions |
. . . . |
. . . |
2 |
|
||
3 |
Base erosion minimum tax amount (attach Form 8991) |
. . . . |
. . . |
3 |
|
||
4 |
Add lines 2 and 3 |
. . . . |
. . . |
4 |
|
||
5a |
Foreign tax credit (attach Form 1118) |
5a |
|
|
|
|
|
b |
Credit from Form 8834 (see instructions) |
5b |
|
|
|
|
|
c |
General business credit (attach Form 3800) |
5c |
|
|
|
|
|
d |
Credit for prior year minimum tax (attach Form 8827) |
5d |
|
|
|
|
|
e |
Bond credits from Form 8912 |
5e |
|
|
|
|
|
6 |
Total credits. Add lines 5a through 5e |
. . . . |
. . . |
6 |
|
||
7 |
Subtract line 6 from line 4 |
. . . . |
. . . |
7 |
|
||
8 |
Personal holding company tax (attach Schedule PH (Form 1120)) |
. . . . |
. . . |
8 |
|
||
9a |
Recapture of investment credit (attach Form 4255) |
9a |
|
|
|
|
|
b |
Recapture of |
9b |
|
|
|
|
|
c |
Interest due under the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form 8697) |
9c |
|
|
|
|
|
d |
Interest due under the |
9d |
|
|
|
|
|
e |
Alternative tax on qualifying shipping activities (attach Form 8902) |
9e |
|
|
|
|
|
f |
Interest/tax due under section 453A(c) and/or section 453(l) |
9f |
|
|
|
|
|
g |
Other (see |
9g |
|
|
|
|
|
10 |
Total. Add lines 9a through 9g |
. . . . |
. . . |
10 |
|
||
11 |
Total tax. Add lines 7, 8, and 10. Enter here and on page 1, line 31 |
. . . . |
. . . |
11 |
|
||
Part
12 Reserved for future use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12
Part
13 |
2020 overpayment credited to 2021 |
. . . . . . . . |
13 |
|
|
||
14 |
2021 estimated tax payments |
. . . . . . . . |
14 |
|
|
||
15 |
2021 refund applied for on Form 4466 |
. . . . . . . . |
15 |
( |
) |
||
16 |
Combine lines 13, 14, and 15 |
. . . . . . . . |
16 |
|
|
||
17 |
Tax deposited with Form 7004 |
. . . . . . . . |
17 |
|
|
||
18 |
Withholding (see instructions) |
. . . . . . . . |
18 |
|
|
||
19 |
Total payments. Add lines 16, 17, and 18 |
. . . . . . . . |
19 |
|
|
||
20 |
Refundable credits from: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
a |
Form 2439 |
|
20a |
|
|
|
|
b |
Form 4136 |
|
20b |
|
|
|
|
c |
Reserved for future use |
|
20c |
|
|
|
|
d |
Other (attach |
|
20d |
|
|
|
|
21 |
Total credits. Add lines 20a through 20d |
. . . . . . . . |
21 |
|
|
||
22 |
Reserved for future use |
. . . . . . . . |
22 |
|
|
||
23 |
Total payments and credits. Add lines 19 and 21. Enter here and on page 1, line 33 . |
. . . . . . . . |
23 |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Form 1120 (2021) |
Form 1120 (2021) |
Page 4 |
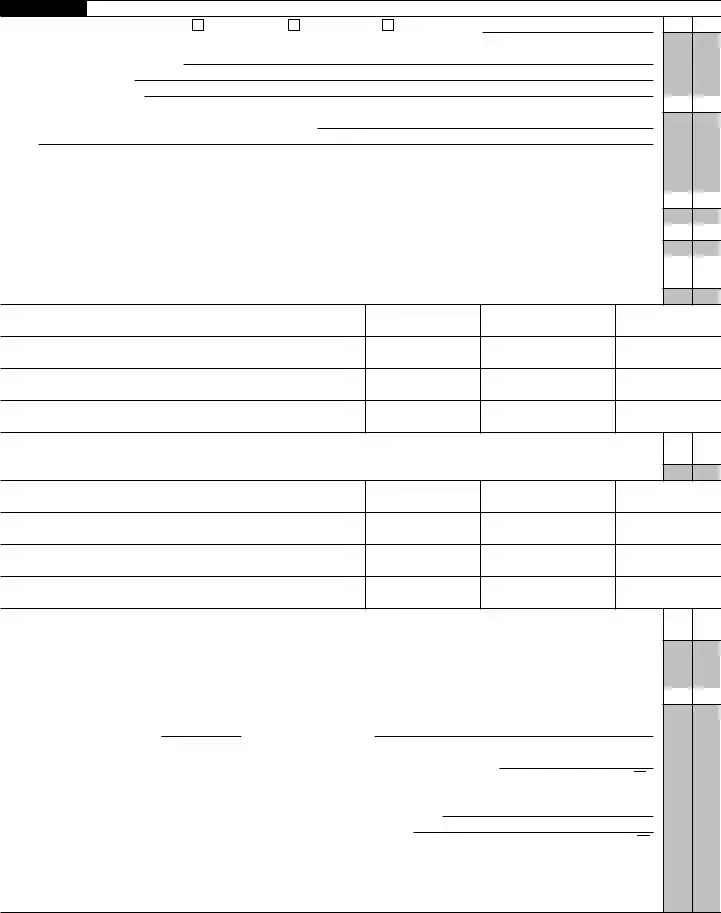
Schedule K Other Information (see instructions)
1 |
Check accounting method: a |
Cash |
b |
Accrual |
c |
Other (specify) ▶ |
2See the instructions and enter the: a Business activity code no. ▶
b Business activity ▶ c Product or service ▶
3 Is the corporation a subsidiary in an affiliated group or a
If “Yes,” enter name and EIN of the parent corporation ▶
4At the end of the tax year:
aDid any foreign or domestic corporation, partnership (including any entity treated as a partnership), trust, or
corporation’s stock entitled to vote? If “Yes,” complete Part I of Schedule G (Form 1120) (attach Schedule G) . . . . . .
bDid any individual or estate own directly 20% or more, or own, directly or indirectly, 50% or more of the total voting power of all
classes of the corporation’s stock entitled to vote? If “Yes,” complete Part II of Schedule G (Form 1120) (attach Schedule G) .
5At the end of the tax year, did the corporation:
aOwn directly 20% or more, or own, directly or indirectly, 50% or more of the total voting power of all classes of stock entitled to vote of any foreign or domestic corporation not included on Form 851, Affiliations Schedule? For rules of constructive ownership, see instructions. If “Yes,” complete (i) through (iv) below.
Yes No
(i)Name of Corporation
(ii)Employer
Identification Number
(if any)
(iii)Country of Incorporation
(iv)Percentage Owned in Voting
Stock
bOwn directly an interest of 20% or more, or own, directly or indirectly, an interest of 50% or more in any foreign or domestic partnership (including an entity treated as a partnership) or in the beneficial interest of a trust? For rules of constructive ownership, see instructions. If “Yes,” complete (i) through (iv) below.
(i)Name of Entity
(ii)Employer
Identification Number
(if any)
(iii)Country of Organization
(iv)Maximum
Percentage Owned in Profit, Loss, or Capital
6During this tax year, did the corporation pay dividends (other than stock dividends and distributions in exchange for stock) in
excess of the corporation’s current and accumulated earnings and profits? See sections 301 and 316 . . . . . . . .
If “Yes,” file Form 5452, Corporate Report of Nondividend Distributions. See the instructions for Form 5452. If this is a consolidated return, answer here for the parent corporation and on Form 851 for each subsidiary.
7At any time during the tax year, did one foreign person own, directly or indirectly, at least 25% of the total voting power of all classes of the corporation’s stock entitled to vote or at least 25% of the total value of all classes of the corporation’s stock? .
For rules of attribution, see section 318. If “Yes,” enter:
(a) Percentage owned ▶ |
and (b) Owner’s country ▶ |
(c)The corporation may have to file Form 5472, Information Return of a 25%
8 Check this box if the corporation issued publicly offered debt instruments with original issue discount . . . . . . ▶ 
 If checked, the corporation may have to file Form 8281, Information Return for Publicly Offered Original Issue Discount Instruments.
If checked, the corporation may have to file Form 8281, Information Return for Publicly Offered Original Issue Discount Instruments.
9Enter the amount of
10Enter the number of shareholders at the end of the tax year (if 100 or fewer) ▶
11If the corporation has an NOL for the tax year and is electing to forego the carryback period, check here (see instructions) ▶ 

If the corporation is filing a consolidated return, the statement required by Regulations section
12Enter the available NOL carryover from prior tax years (do not reduce it by any deduction reported on
page 1, line 29a.) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ▶ $
Form 1120 (2021)

Form 1120 (2021) |
Page 5 |
Schedule K Other Information (continued from page 4)
13 |
Are the corporation’s total receipts (page 1, line 1a, plus lines 4 through 10) for the tax year and its total assets at the end of the |
Yes No |
|
||
|
tax year less than $250,000? |
|
|
If “Yes,” the corporation is not required to complete Schedules L, |
|
|
distributions and the book value of property distributions (other than cash) made during the tax year ▶ $ |
|
14 |
Is the corporation required to file Schedule UTP (Form 1120), Uncertain Tax Position Statement? See instructions . . . . |
|
|
If “Yes,” complete and attach Schedule UTP. |
|
15a |
Did the corporation make any payments in 2021 that would require it to file Form(s) 1099? |
|
b |
If “Yes,” did or will the corporation file required Form(s) 1099? |
|
16During this tax year, did the corporation have an
own stock? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
17During or subsequent to this tax year, but before the filing of this return, did the corporation dispose of more than 65% (by value)
of its assets in a taxable,
18Did the corporation receive assets in a section 351 transfer in which any of the transferred assets had a fair market basis or fair
market value of more than $1 million? . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
19During the corporation’s tax year, did the corporation make any payments that would require it to file Forms 1042 and
20 Is the corporation operating on a cooperative basis?. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
21During the tax year, did the corporation pay or accrue any interest or royalty for which the deduction is not allowed under section
267A? See instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
If “Yes,” enter the total amount of the disallowed deductions ▶ $
22Does the corporation have gross receipts of at least $500 million in any of the 3 preceding tax years? (See sections 59A(e)(2)
and (3)) . |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
. |
If “Yes,” complete and attach Form 8991.
23Did the corporation have an election under section 163(j) for any real property trade or business or any farming business in effect
|
during the tax year? See instructions |
24 |
Does the corporation satisfy one or more of the following? See instructions |
aThe corporation owns a
bThe corporation’s aggregate average annual gross receipts (determined under section 448(c)) for the 3 tax years preceding the current tax year are more than $26 million and the corporation has business interest expense.
cThe corporation is a tax shelter and the corporation has business interest expense. If “Yes,” complete and attach Form 8990.
25 |
Is the corporation attaching Form 8996 to certify as a Qualified Opportunity Fund? |
|
If “Yes,” enter amount from Form 8996, line 15 . . . . ▶ $ |
26Since December 22, 2017, did a foreign corporation directly or indirectly acquire substantially all of the properties held directly or indirectly by the corporation, and was the ownership percentage (by vote or value) for purposes of section 7874 greater than 50% (for example, the shareholders held more than 50% of the stock of the foreign corporation)? If “Yes,” list the ownership
percentage by vote and by value. See instructions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Percentage: By Vote |
By Value |
Form 1120 (2021)
Form 1120 (2021) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Page 6 |
||
Schedule L |
|
Balance Sheets per Books |
|
|
Beginning of tax year |
|
|
End of tax year |
|
||||||
|
|
|
Assets |
|
|
|
|
(a) |
|
(b) |
|
(c) |
|
|
(d) |
1 |
Cash |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
2a |
Trade notes and accounts receivable . . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
b |
Less allowance for bad debts . . |
. . . |
|
( |
|
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
||||
3 |
Inventories |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
4 |
U.S. government obligations |
. . . . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
6 |
Other current assets (attach statement) . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
7 |
Loans to shareholders |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
8 |
Mortgage and real estate loans |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
9 |
Other investments (attach statement) . . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
10a |
Buildings and other depreciable assets . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
b |
Less accumulated depreciation . . |
. . . |
|
( |
|
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
||||
11a |
Depletable assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
b |
Less accumulated depletion . . . |
. . . |
|
( |
|
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
||||
12 |
Land (net of any amortization) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
13a |
Intangible assets (amortizable only) |
. . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
b |
Less accumulated amortization . . |
. . . |
|
( |
|
) |
|
( |
) |
|
|
||||
14 |
Other assets (attach statement) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
15 |
Total assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
16 |
Accounts payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
17 |
Mortgages, notes, bonds payable in less than 1 year |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
18 |
Other current liabilities (attach statement) . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
19 |
Loans from shareholders |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
20 |
Mortgages, notes, bonds payable in 1 year or more |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
21 |
Other liabilities (attach statement) . . . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
22 |
Capital stock: |
a Preferred stock . . . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
b Common stock . . . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
23 |
Additional |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
24 |
Retained |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
25 |
Retained |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
26 |
Adjustments to shareholders’ equity (attach statement) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
27 |
Less cost of treasury stock |
|
|
|
|
( |
) |
|
|
( |
) |
||||
28 |
Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity . . |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Schedule
Note: The corporation may be required to file Schedule
1 |
Net income (loss) per books |
7 |
Income recorded on books this year |
|
2 |
Federal income tax per books |
|
|
not included on this return (itemize): |
3 |
Excess of capital losses over capital gains . |
|
|
|
4Income subject to tax not recorded on books this year (itemize):
|
|
|
8 |
|
Deductions on this return not charged |
5 |
Expenses recorded on books this year not |
|
against book income this year (itemize): |
||
|
deducted on this return (itemize): |
a |
Depreciation . . $ |
||
a |
Depreciation . . . . $ |
b |
Charitable contributions $ |
||
bCharitable contributions . $
cTravel and entertainment . $
|
|
|
9 |
Add lines 7 and 8 |
6 |
Add lines 1 through 5 |
10 |
Income (page 1, line |
|
Schedule
1 |
Balance at beginning of year |
5 |
Distributions: a Cash |
||
2 |
Net income (loss) per books |
|
|
|
b Stock . . . . |
3 |
Other increases (itemize): |
|
|
|
c Property . . . . |
|
|
|
6 |
Other decreases (itemize): |
|
|
|
|
7 |
Add lines 5 and 6 |
|
4 |
Add lines 1, 2, and 3 |
8 |
Balance at end of year (line 4 less line 7) |
||
Form 1120 (2021)
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the IRS Form 1120?
The IRS Form 1120 is the U.S. Corporation Income Tax Return. Corporations, including C corporations, must file this form annually to report their income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits. It is essential for determining the corporation's tax liability for the year.
-
Who is required to file Form 1120?
All domestic corporations are required to file Form 1120, regardless of whether they have taxable income or not. This includes C corporations, which are taxed separately from their owners, as well as certain other entities that may be classified as corporations for tax purposes.
-
When is Form 1120 due?
Form 1120 is generally due on the 15th day of the fourth month after the end of the corporation’s tax year. For corporations operating on a calendar year, this means the deadline is April 15. If the due date falls on a weekend or holiday, the deadline extends to the next business day.
-
What information is needed to complete Form 1120?
To accurately complete Form 1120, a corporation needs various pieces of information, including:
- Gross receipts or sales
- Cost of goods sold
- Operating expenses
- Tax credits and deductions
- Details of any assets and liabilities
Having accurate financial records is crucial for filling out this form correctly.
-
Can a corporation request an extension for filing Form 1120?
Yes, a corporation can request an automatic six-month extension to file Form 1120 by submitting Form 7004. However, it is important to note that this extension only applies to the filing of the form, not to the payment of any taxes owed. Corporations must estimate their tax liability and pay any amount due by the original due date to avoid penalties.
-
What happens if a corporation fails to file Form 1120?
Failure to file Form 1120 can result in significant penalties. The IRS may impose a penalty of up to $210 for each month the return is late, up to a maximum of 12 months. Additionally, interest will accrue on any unpaid taxes. It is crucial for corporations to file on time to avoid these consequences.
-
Are there any special considerations for foreign corporations?
Foreign corporations that engage in business within the United States may have different filing requirements. They typically need to file Form 1120-F, which is specifically designed for foreign corporations. Understanding the nuances of U.S. tax law is essential for these entities to ensure compliance.
-
Where can I find assistance for completing Form 1120?
Corporations can seek assistance from various sources when completing Form 1120. Certified public accountants (CPAs) and tax professionals can provide valuable guidance. Additionally, the IRS website offers resources, including instructions for Form 1120, which can be beneficial for understanding the filing process.
Misconceptions
The IRS Form 1120 is essential for corporations to report their income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits. However, several misconceptions exist about this form. Here are eight common misunderstandings:
- Only large corporations need to file Form 1120. Many believe that only large corporations are required to file this form. In reality, any corporation, regardless of size, must file Form 1120 if it is recognized as a corporation by the IRS.
- Form 1120 is only for C Corporations. Some think that Form 1120 applies solely to C Corporations. However, S Corporations use a different form (1120S), while C Corporations use Form 1120.
- Filing Form 1120 guarantees a refund. Many assume that submitting Form 1120 will automatically result in a tax refund. Refunds depend on various factors, including overpayment of taxes, not merely the act of filing.
- All income must be reported on Form 1120. Some individuals believe that only income from business operations needs to be reported. All income, including investments and passive income, should be reported on the form.
- Form 1120 can be filed at any time. There is a misconception that corporations can file Form 1120 whenever they choose. In fact, it must be filed on or before the 15th day of the fourth month following the end of the corporation's tax year.
- Filing Form 1120 is a one-time event. Some think that once a corporation files Form 1120, they do not need to file again. Corporations must file annually, regardless of whether they had a profit or loss.
- Using a tax professional is unnecessary. Many believe they can complete Form 1120 without assistance. While some may manage it independently, consulting a tax professional can help ensure accuracy and compliance with current tax laws.
- Form 1120 is the same for every state. Some assume that Form 1120 is uniform across all states. However, state tax laws can vary significantly, and additional state forms may be required.
Understanding these misconceptions can help corporations navigate their tax responsibilities more effectively. It is crucial to approach tax filing with accurate information to avoid penalties and ensure compliance.
Common mistakes
-
Failing to enter the correct Employer Identification Number (EIN). The EIN is crucial for identifying the corporation. Without it, the IRS may reject the form.
-
Omitting necessary financial information. Complete and accurate reporting of income, deductions, and credits is essential. Missing figures can lead to discrepancies.
-
Incorrectly calculating tax liability. Many people miscalculate their tax obligations, which can result in underpayment or overpayment.
-
Neglecting to sign and date the form. A signature is a requirement for the form to be valid. An unsigned form may be considered incomplete.
-
Using outdated forms. Tax laws change frequently, and using an old version of the form can lead to compliance issues.
-
Not keeping copies of submitted forms. Retaining copies is important for record-keeping and future reference in case of audits or inquiries.
-
Ignoring deadlines. Timely submission is critical. Late filings can result in penalties and interest charges.
-
Overlooking state tax obligations. While the IRS form is federal, many states have additional requirements that must also be addressed.
Additional PDF Templates
Dnd 5e Fillable Character Sheet - A crusader for justice, unafraid to stand alone.
To establish a secure understanding between parties regarding confidential information, a Non-disclosure Agreement form is essential. This legal contract not only clarifies the responsibilities of each party but also ensures that sensitive data remains protected. For those seeking to formalize this agreement and understand its implications further, resources such as OnlineLawDocs.com can provide valuable insights.
96 Well Plate Diagram - Can hold reagents, samples, or controls in medical diagnostics.
Document Data
| Fact Name | Details |
|---|---|
| Purpose | The IRS Form 1120 is used by corporations to report their income, gains, losses, deductions, and credits. |
| Filing Requirement | Corporations must file Form 1120 if they are subject to federal income tax. |
| Due Date | The form is typically due on the 15th day of the 4th month after the end of the corporation's tax year. |
| Estimated Tax Payments | Corporations may need to make estimated tax payments throughout the year to avoid penalties. |
| State-Specific Forms | Many states require their own corporate tax forms, such as California's Form 100, governed by California Revenue and Taxation Code. |
| Electronic Filing | Corporations can file Form 1120 electronically, which may speed up processing times. |
| Amended Returns | If errors are found after filing, corporations can submit Form 1120-X to amend their return. |
| Record Keeping | Corporations must keep records for at least three years after filing Form 1120, in case of audits. |
Similar forms
The IRS Form 1120 is the annual income tax return filed by corporations in the United States. A similar document is the IRS Form 1065, which is used by partnerships. Both forms serve the purpose of reporting income, deductions, and tax liabilities to the IRS. However, while Form 1120 is for corporations, Form 1065 is specifically designed for partnerships, which pass their income through to individual partners for tax purposes. This distinction highlights the different structures of these business entities and how they are taxed under federal law.
Another document akin to the IRS Form 1120 is the IRS Form 1040, the individual income tax return. While Form 1120 focuses on corporate income, Form 1040 is used by individual taxpayers to report their earnings and calculate their personal tax obligations. Both forms require detailed reporting of income and deductions, but they cater to different types of taxpayers. Understanding the nuances between these forms is essential for individuals and businesses alike when navigating their tax responsibilities.
A New York Lease Agreement form is a legal document that outlines the terms and conditions between a landlord and a tenant for renting a residential or commercial property. This form serves as a binding contract, detailing essential elements such as rental price, lease duration, and the responsibilities of both parties. Understanding this document is crucial for protecting rights and ensuring a smooth rental experience. For more information, you can visit https://documentonline.org/blank-new-york-lease-agreement/.
The IRS Form 990 is also comparable to Form 1120, but it is specifically for tax-exempt organizations. Like Form 1120, Form 990 requires organizations to disclose their financial activities, including revenue and expenses. This transparency helps the IRS and the public understand how these organizations operate. While Form 1120 is concerned with taxable income, Form 990 focuses on ensuring that tax-exempt entities adhere to regulations and maintain their non-profit status.
Similarly, the IRS Form 941 is another document that shares some characteristics with Form 1120. Form 941 is used by employers to report payroll taxes withheld from employees' wages. Both forms require accurate reporting and adherence to tax laws, but they serve different purposes. Form 941 is filed quarterly, focusing on employment taxes, while Form 1120 is an annual return that addresses corporate income taxes. Understanding these forms is crucial for businesses managing their financial obligations.
Lastly, the IRS Form 1120-S is a close relative of Form 1120, as it is used by S corporations. Both forms are designed for corporations, but they differ in tax treatment. An S corporation allows income to pass through to shareholders, avoiding double taxation. Like Form 1120, Form 1120-S requires detailed financial reporting, but it also necessitates additional information about the distribution of income to shareholders. This distinction is vital for corporations considering their tax strategies and structure.